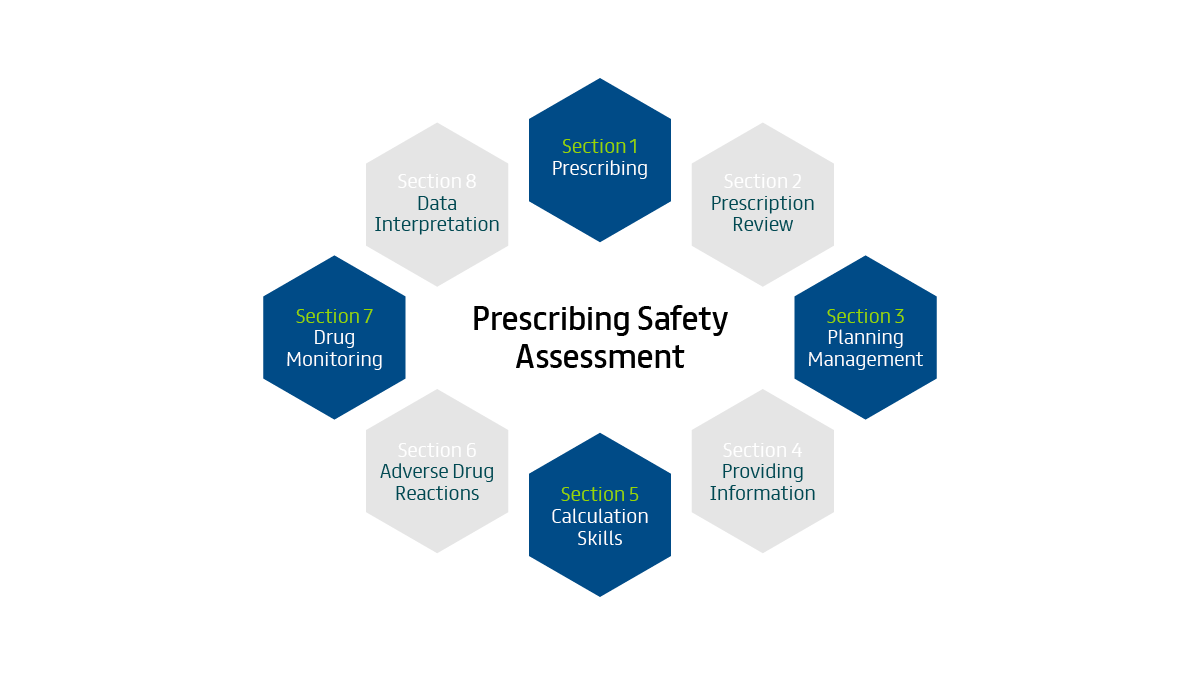
There are 8 sections of the Prescribing Safety Assessment, each testing a different area of prescribing competency. Some sections are weighted more heavily than others, and some have a different number of question items than others.
In order to prepare for your PSA exam, it’s important that you familiarise yourself with each of the 8 sections of the exam, so you know what’s expected of you and where you might find the most marks.
Weighting Of PSA Exam Questions
There are 200 marks available in total, broken down across the 8 sections of the PSA as follows:
- Section 1: Prescribing (PWS) is worth 80 marks (8 question items worth 10 marks each)
- Section 2: Prescription Review (REV) is worth 32 marks (8 question items worth 4 marks each)
- Section 3: Planning Management (MAN) is worth 16 marks (8 question items worth 2 marks each)
- Section 4: Providing Information (COM) is worth 12 marks (6 question items worth 2 marks each)
- Section 5: Calculation Skills (CAL) is worth 16 marks (8 question items worth 2 marks each)
- Section 6: Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR) is worth 16 marks (8 question items worth 2 marks each)
- Section 7: Drug Monitoring (TDM) is worth 16 marks (8 question items worth 2 marks each)
- Section 8: Data Interpretation (DAT) is worth 12 marks (6 question items worth 2 marks each)
PSA Sections Explained
Each section of the PSA is designed to test a different area of prescribing. In a nutshell, that means:
Section 1: Prescribing (PWS) tests your ability to write a safe and effective prescription, to manage acute medical emergencies, and to plan appropriate drug therapy for common indications.
Section 2: Prescription Review (REV) tests your ability to review the prescribing of others, to spot potentially important errors and to make changes that will improve patient outcomes.
Section 3: Planning Management (MAN) tests your ability to plan appropriate treatment for common clinical indications.
Section 4: Providing Information (COM) tests your ability to provide patients with important information about their medicines.
Section 5: Calculation Skills (CAL) tests your ability to calculate appropriate drug doses and record the outcome accurately.
Section 6: Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR) tests your ability to detect, respond to and prevent potential adverse drug reactions.
Section 7: Drug Monitoring (TDM) tests your knowledge of how drugs work and their clinical effects, and your ability to monitor them appropriately to maximise safety and efficacy.
Section 8: Data Interpretation (DAT) tests your ability to interpret data on the impact of drug therapy and make appropriate changes, as well as critically appraising the results of relevant diagnostic, prognostic and treatment trials.
PSA Sections Explained By The Experts
For a more detailed outline of what’s in the PSA, check out our What’s In The PSA Exam blog post. However, the best way to prepare is to watch PSA Prep, a set of 9 (totally free) eLearning sessions we’ve created for exam candidates, working with a team of experts.
There’s a dedicated PSA Prep session for each of the 8 sections, providing you with a detailed outline of the section and addressing some of the biggest challenges faced by PSA candidates, such as coping with the time pressures, managing the calculations and identifying the key points in each clinical scenario.
For instant access, simply create (or log in to) your BPS Assessment portal account and scroll down to ‘PSA Prep’.